Spring与动态代理机制
本站字数:108k 本文字数:1.9k 预计阅读时长:7min 访问次数:次Spring AOP 在 Spring 框架中起到了非常重要的作用,例如在处理一个事务的时候,遇到的 @Transactional 注解;亦或是在处理重要业务的时候,做一些日志处理。这些操作可能对于增删改都是公用的,但是却很难使用面向对象的机制来解决这个问题。正因为此 AOP 应运而生。本篇主要讨论关于Spring AOP机制以及动态代理机制。
动态代理机制
Java中的动态代理主要分为两大门派,一个是Jdk根正苗红的Jdk动态代理,另一个就是充满黑魔法气息的CGLIB字节码动态代理。两种方式各有优缺点,两种方式也是没办法相互替代的,所以,在Spring中,基于对两者的优缺点,以及应用范围,有了不同的选择。
JDK动态代理
JDK动态代理基于接口进行代理,如果一个类没有实现任何接口,但是还想要使用JDK动态代理的话,建议抽取出一个接口,然后使用动态代理机制。
JDK动态代理基于接口的实现,达到代理的目的,重要参数:
classLoader:类加载器interfaces:代理的接口InvocationHandler:执行时触发的处理器
下面就是一段典型的JDK动态代理的代码实现,用于获取JDK动态代理对象:
1 | (Foo) Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, new Class[]{Foo.class}, (proxy, method, args1) -> { |
CGLIB动态代理
CGLIB动态代理是基于继承机制实现的代理。如果一个类没有实现任何接口,或者是实现了接口,都可以使用CGLIB来进行动态代理。但是随着JDK的不断发展,CGLIB的性能也很难去赶上JDK动态代理的性能,但是功能上,还是比JDK动态代理强不少的。
CGLIB既然是基于继承机制实现的代理,那么就会出现在集成上无法代理的问题,比如,类是 final 的,这样的类无法被继承,只能通过JDK动态代理来实现代理。同理,还有方法被标识为 final 的无法被增强。
CGLIB的另一个优势还在于,执行方法的时候有多种选择,可以通过反射的方式执行,或者通过MethodProxy来执行。
Enhancer是CGLIB一个重要的类,生成代理对象的时候,重要参数有:
type- 代理的类的类型invocation- 执行代理对象时候的回调函数,一般指的是MethodCallback
下面是一个典型的生成CGLIB代理对象的代码段:
1 | (Target) Enhancer.create(Target.class, (MethodInterceptor) (proxy, method, objects, methodProxy) -> { |
两种动态代理的比较
JDK代理一种方式测试,CGLIB三种测试方法,测试执行 100, 000, 000 次,取10次运行结果的平均值。
- JDK动态代理
- CGLIB - 利用反射执行:
(proxy, method, objects, methodProxy) -> method.invoke(target, objects) - CGLIB - 利用MethodProxy和目标对象执行:
(proxy, method, objects, methodProxy) -> methodProxy.invoke(target, objects) - CGLIB - 利用MethodProxy和代理对象执行:
(proxy, method, objects, methodProxy) -> methodProxy.invokeSuper(proxy, objects)
1 | interface Interface { |
| 测试方法 | 执行时间平均值 |
|---|---|
| JDK动态代理 | 330.1ms |
| CGLIB - 利用反射执行 | 326.4ms |
| CGLIB - 利用MethodProxy和目标对象执行(Spring) | 249.1ms |
| CGLIB - 利用MethodProxy和代理对象执行 | 198ms |
结果上还是比较明显的,JDK动态代理还是比CGLIB慢一些。JDK动态代理使用反射调用方法,CGLIB第一种方式也是使用反射调用方法,所以两者之间差异并不是很大。但是CGLIB后面的两种方法,对于执行速度有了很大程度上的提高。
Spring AOP机制与动态代理
Spring 的AOP主要由:切点(Pointcut),通知(Advise)和切面(Advisor)构成,最后通过AopProxyFactory生成代理对象。本文主要介绍,如何进行最基本的切面编程以及 Spring 在 JDK 动态代理和CGLIB动态代理之间做选择的。
Spring AOP的简单流程
- 准备切点(Pointcut)
- 准备通知(Advise)
- 准备切面(Advisor)
- 生成代理对象
代码的接口和目标类型代码如下:
1 | interface Interface { |
下面的代码不需要过多的解释,代码实现如下所示:
1 | // 准备切点 |
Spring AOP对于代理方式的选择
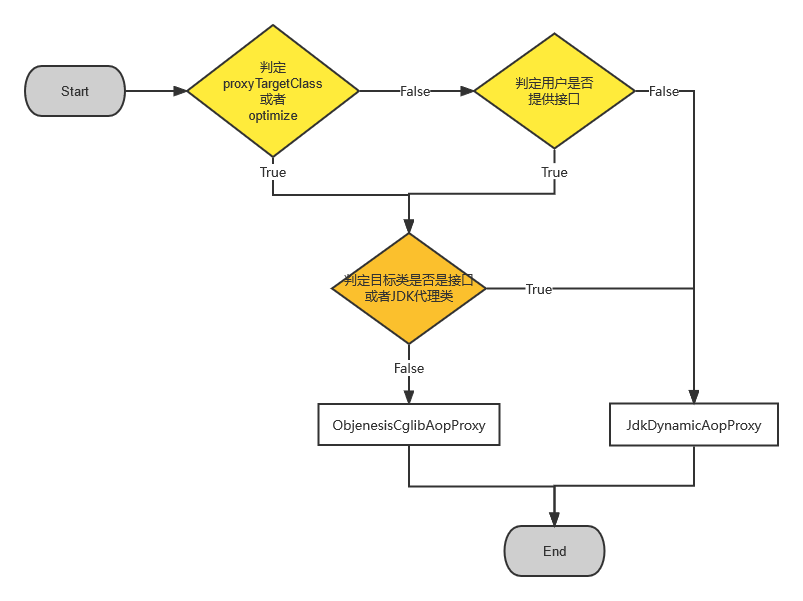
Spring在采用动态代理的方案选择上,同时使用JDK动态代理和CGLIB动态代理两种方式,但是对于动态代理的选择上面做了诸多考量,代码如下:
1 |
|
条件一:
!NativeDetector.inNativeImage()判断是不是Native的镜像,如果是那就是用JDK动态代理
条件二:
config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config))上面条件依次判断,
optimize参数默认是false,proxyTargetClass参数默认是false,这两个参数可以断定是不是要使用CGLIB。当两个参数都是false的时候,才会判断第三个条件hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)。条件三:
hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)这个条件是所有条件中比较难以理解的一个条件,这个方法的内容如下
hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces方法 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9/**
* Determine whether the supplied {@link AdvisedSupport} has only the
* {@link org.springframework.aop.SpringProxy} interface specified
* (or no proxy interfaces specified at all).
*/
private boolean hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(AdvisedSupport config) {
Class<?>[] ifcs = config.getProxiedInterfaces();
return (ifcs.length == 0 || (ifcs.length == 1 && SpringProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(ifcs[0])));
}这个方法,首先获取到配置中的需要被代理的接口数组,然后判定这个接口数组是否是空,或者当且仅当只有一个接口
SpringProxy.class只有在这种情况下为真,如果这个方法为假,那么将使用JDK动态代理的方式执行。那么这个所谓 “用户指定的接口” 是在哪里指定的呢?在 [如上代码](#Spring AOP的简单流程) 注释上已经说明。
条件四:进入 if 中,获取目标类类型是不是接口,或者是Jdk代理类型,如果是,那就选择JDK动态代理;否则使用CGLIB动态代理
上面的条件,除了条件一,其他条件才是判定的核心,转化为流程图可以如图表示: